Formulas for Calculating Conduit & Pipe Bends
Calculations & Formulas
Using just a few mathematical formulas allows you to properly calculate a bend of nearly any angle. An inexpensive scientific calculator and an angle finder are the only additional tools required. When calculating bend allowances to determine the cut length of HDPE conduit or PVC pipe, one must calculate from the center line radius (CLR) of the finished, bent pipe. This radius will vary depending on the outside diameter of the tube, the wall thickness, and the angle at which the tube is to be bent.
Elements of a Bend
It is important to understand the different elements of a bend in order to make accurate calculations.
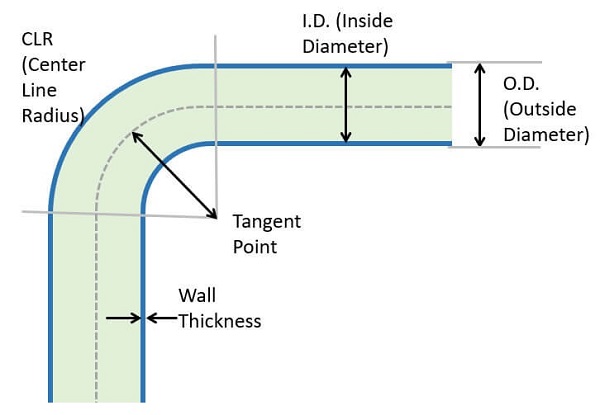
Calculating Wall Thickness
ISO 161-1 uses the following formula to calculate the wall thickness of pipe:
σs=PN.(da-s/20.s)=PN.S
σs = hoop stress (N/mm2) | PN = normal pressure (bar) | da = external pipe diameter (mm)
s = wall thickness (mm) | S = pipe serial (-)
Calculating Standard Dimension Ratio
Using the same variables as above, the standard dimension ratio (SDR) of a pipe can be calculated thusly:
SDR = da/s
| HDPE Pipe SDR | Minimum Long-Term Cold Bending Radius |
| 9 or less | 20x pipe OD |
| 11, 13.5 | 25x pipe OD |
| 15.5, 17, 21 | 27x pipe OD |
| 26 | 34x pipe OD |
| 32.5 | 42x pipe OD |
| 41 | 52x pipe OD |
| With fitting or flange present in bend | 100x pipe OD |
Calculating CLR (Center Line Radius) for Bend Angle
After you've selected the appropriate die for bending your pipe, based on the pipe's outside diameter and wall thickness, you should be able to find the radius of the bend.
A simple way to determine the center line radius of a bend of a specific angle is calculate a full circle, then divide that number by 360 to find the measurement of one degree. Then, use this formula:
π(2r) or πD
π (pi) = 3.1416
For example, if your die creates a 2.2" radius, and you need to create a 35° bend, your calculations would look something like this:
to calculate one degree of bend
3.1416(2x2.2) = 13.823/360 = 0.0384
to calculate CLR of 35° bend
0.0384 x 35 = 1.344"
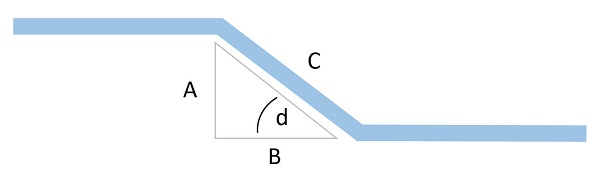
Offset Bend Calculation
3-Point Saddle Bend Calculation
 4-Point Saddle Bend Calculation
4-Point Saddle Bend Calculation
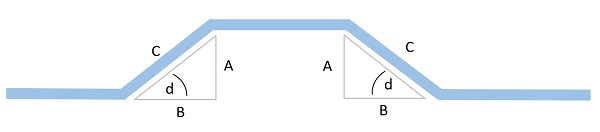
Most bends other than 90° can be calculated using the geometry of a triangle. The black line represents an offset bend in a tube; the red triangle represents the triangular geometry this offset creates.
The lengths/sides of the triangle are labeled "a," "b," and "c". The "d" represents the angle at which the pipe is bent. No matter how the tube is bent in this configuration (or how the triangle is oriented), one of the angles of the triangle will be 90°; the other angle will depend on the first angle (d), and can be calculated as (90 – d).
The relatively simple math formulas of sine, cosine, and tangent can be used to determine the angles of the triangle, and, therefore, the necessary angles of your pipe bend(s). Most scientific calculators (and even the calculators built into smart phones) have these functions.
Sine Calculation
Sine(d) = A/C
A = sine(d) x C
C = A/sine(d)
Cosine Calculation
Cos(d) = B/C
B = cos(d) x C
C = B/cos(d)
Tangent Calculation
Tan(d) = A/B
A = tan(d) x B
B = A/tan(d)
View information about bending conduit using a bender and the deducts and multipliers charts.
Other Articles You Might Enjoy:
How to Estimate HDPE Conduit Runs
How to Pull Wire Through Conduit
Choosing the Right Pipe for Underground Utility Applications
